แม่ๆหลายคนต้องเจอกับความผิดหวังจากการทำเด็กหลอดแก้ว (ICSI) ใส่ตัวอ่อนแล้วไม่ติดสมหวังดังใจ บางคนย้ายมาแล้วหลายครั้งก็ยังไม่ติด
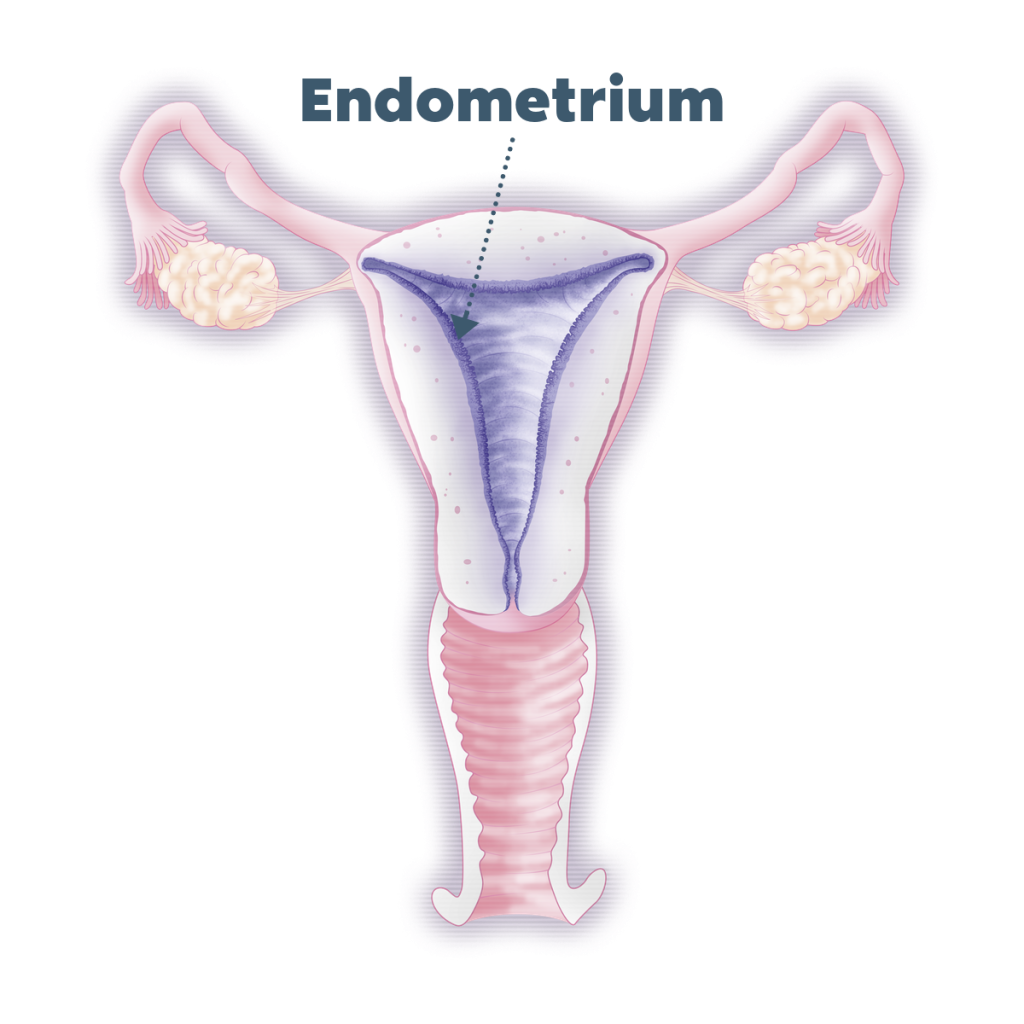
ซึ่งปัจจัยในเรื่องเซลล์ไข่ที่ไม่สมบูรณ์และผนังมดลูกไม่พร้อมเป็นสาหตุหลัก ยังรวมไปถึงความไม่สมดุลของฮอร์โมน และปัญหาภายในอวัยวะสืบพันธุ์ของแม่ๆ ก็เป็นสาเหตุที่อาจส่งผลต่อการขัดขวางการฝังตัวของตัวอ่อนได้
ในการทำเด็กหลอดแก้ว (ICSI) นั้นหลังจากที่ทำการดูดไข่ออกมาจากตัวคุณแม่แล้วก็จะนำไข่มาปฏิสนธิภายนอก หลังจากนั้นก็จะมีการเลี้ยงตัวอ่อนในห้องปฏิบัติการเพื่อให้ตัวอ่อนแบ่งเซลล์จนถึงขนาดที่เหมาะสมที่จะสามารถย้ายตัวอ่อนกลับเข้าสู่โพรงมดลูกได้
มีคำถามว่าตัวอ่อนระยะที่แตกต่างกันส่งผลต่อโอกาสในการตั้งครรภ์ที่แตกต่างกันหรือไม่
และตัวอ่อน Day5 หรือบลาสโตซิสต์ส่งผลให้โอกาสตั้งครรภ์สูงขึ้นจริงหรือ
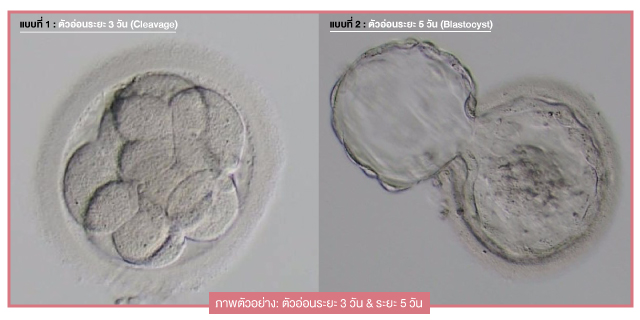
การพัฒนาการของตัวอ่อนมนุษย์ จะเริ่มจากเซลล์หนึ่งเซลล์ เป็นสอง เป็นสี่ เป็นแปด เป็นสิบหก โดยเรียกชื่อระยะต่างๆตามจำนวนวันที่เพาะเลี้ยงได้แก่
ตัวอ่อนDay 1 (ระยะไซโกต, Zygote)
ตัวอ่อนDay 3 (ระยะคลีเวจ, Cleavage)
ตัวอ่อนDay 5 (ระยะบลาสโตซิสต์, Blastocyst)
#ตัวอ่อนระยะบลาสโตซิสต์ (Blastocyst) เป็นตัวอ่อนที่เกิดจากการปฏิสนธิของไข่และอสุจิซึ่งเลี้ยงให้เติบโตในห้องปฏิบัติการมาได้อายุ 5-6 วัน จะมีเซลล์จำนวน 80-120 เซลล์ ตัวอ่อนระยะบลาสโตซิสต์จะมีเซลล์ต้นกำเนิดและเซลล์รกที่พร้อมฝังตัวสู่โพรงมดลูก #จึงเรียกได้ว่าเป็นระยะพร้อมฝังตัว
ตัวอ่อน “ระยะบลาสโตซิสต์” ถือว่าเติบโตได้ดีในระดับหนึ่ง ซึ่งจะมีวิธีการแบ่งเกรดตัวอ่อนออกเป็น A B C อีกเพราะไม่ใช่ว่าตัวอ่อนระยะนี้จะเป็นตัวอ่อนที่ดีหมดทุกตัว ยังต้องมีการคัดเลือกอีกครั้งก่อนย้ายกลับสู่โพรงมดลูก
อย่างไรก็ตามโดยทั่วไปการเลี้ยงตัวอ่อนมาถึงระยะนี้จึงเป็นเหมือน “การคัดกรองตัวอ่อน” ในระดับหนึ่งแล้ว ตัวอ่อนที่เติบโตมาถึงระยะนี้ก็แสดงให้เห็นว่าแข็งแรงในระดับหนึ่ง แพทย์จึงนิยมใส่ตัวอ่อนในระยะ Day 5 เพื่อเพิ่มโอกาสในการตั้งครรภ์ที่สูงขึ้นค่ะ
ข้อดีของตัวอ่อนระยะบลาสโตซิสต์ได้แก่
(1) เป็นการคัดกรองตัวอ่อนคุณภาพดีที่มีออกมาใส่กลับเข้าสู่โพรงมดลูก
เมื่อตัวอ่อนเติบโตมาถึงระยะบลาสโตซิสต์ซึ่งถือเป็นการคัดกรองระดับหนึ่ง จากตัวอ่อนที่มีเรายังแบ่งเกรดจากลักษณะที่พบผ่านกล้องจุลทรรศน์ และคัดเลือกตัวอ่อนที่คุณภาพดีที่สุดที่มีเพื่อย้ายกลับเข้าสู่โพรงมดลูก ซึ่งหากใส่ถูกตัวก็จะลดระยะเวลาของการรอการตั้งครรภ์ลงได้
(2) มีอัตราฝังตัวและตั้งครรภ์สูง
การย้ายกลับตัวอ่อนระยะบลาสโตซิสต์ทางโพรงมดลูกนั้นเหมาะสมที่จะฝังตัวมากที่สุด เนื่องจากในภาวะการตั้งครรภ์โดยธรรมชาตินั้น ตัวอ่อนจะเดินทางไปถึงโพรงมดลูกเพื่อที่จะฝังตัวในระยะบลาสโตซิสต์เช่นกัน แต่ถ้าหากเป็นตัวอ่อนระยะDay 3 (Cleavage) จะเป็นช่วงที่ตัวอ่อนอยู่ในท่อนำไข่ จึงอาจจะยังไม่พร้อมในการฝังตัว ต้องใช้เวลาพัฒนาให้เป็นระยะบลาสโตซิสท์ก่อนจึงจะพร้อมสำหรับการฝังตัวที่โพรงมดลูก นอกจากนั้นระยะคลีเวจอาจมีโอกาสหยุดการเจริญเติบโตก่อนการฝังตัวได้ด้วย
(3) ตัวอ่อนที่คุณภาพดีก็จะช่วยลดอัตราการแท้ง
ส่งผลต่อความสำเร็จกับการตั้งครรภ์ที่สมบูรณ์เพิ่มสูงขึ้น
(4) สามารถตรวจโครโมโซมของตัวอ่อนเพื่อเช็คความผิดปกติได้
เราสามารถดึงเซลล์รกของตัวอ่อนระยะบลาสโตซิสต์เพื่อมาตรวจโครโมโซม 23 คู่ด้วยผลที่แม่นยำถึง 99 % เพื่อตรวจ “ดาวน์ซินโดรม” ในกลุ่มแม่อายุเกิน 35 ปี แม่ที่แท้งบ่อย รวมถึงสามารถตรวจคัดกรองโรคที่ถ่ายทอดทางพันธุกรรม เช่น ธาลัสซีเมียชนิดรุนแรง โดยใช้เทคนิคการตรวจต่างๆ เพิ่มเติม ซึ่งจะช่วยให้มั่นใจมากขึ้นว่าตัวอ่อนมีคุณภาพและไม่มีความผิดปกติแฝงอยู่
ที่สำคัญการตรวจโครโมโซมในระยะนี้ไม่ส่งผลกับการตั้งครรภ์ เนื่องจากการดึงเซลล์จากรกไม่ส่งผลกับตัวอ่อน ต่างจากการตรวจตัวอ่อน Day 3 ที่มีตัวอ่อนเพียง 6-8 เซลล์เมื่อไปดึงเซลล์ออกมาก็อาจส่งผลกับตัวอ่อนและการตั้งครรภ์ได้
(5) ลดการเกิดตั้งครรภ์แฝด
เนื่องจากเป็นการคัดเลือกตัวอ่อนที่ดีที่สุด และเป็นระยะที่พร้อมจะฝังตัว ดังนั้นคุณหมอจึงย้ายตัวอ่อนกลับเพียง 1-2 ตัวเท่านั้น จึงลดความเสี่ยงในการ “ตั้งครรภ์แฝด” ซึ่งถือเป็นภาวะแทรกซ้อนของการทำเด็กหลอดแก้ว เพราะการตั้งครรภ์แฝดมีความเสี่ยงต่อความปลอดภัยของทั้งแม่และทารกในครรภ์หลายประการเช่น ทารกตายในครรภ์ หรือ คลอดก่อนกำหนด เป็นต้น
(6) ตัวอ่อนที่เหลือสามารถเก็บแช่แข็งไว้ได้
การย้ายกลับตัวอ่อนในจำนวนที่น้อยลง ทำให้มีตัวอ่อนคุณภาพดี เหลือเก็บแช่แข็งไว้สำหรับย้ายกลับในรอบถัดๆ ไปได้ค่ะ
สำหรับข้อเสียของการเลี้ยงตัวอ่อนระยะบลาสโตซิสต์อาจจะมีได้ หากมีไข่น้อย แล้วได้ตัวอ่อนไม่มาก การเลี้ยงตัวอ่อนนานไปจนถึงวันที่ 5-6 อาจไม่มีตัวอ่อนเหลือให้ย้ายกลับสู่โพรงมดลูก เนื่องจากตัวอ่อนตายหมดหรือคุณภาพไม่ดี
จากเหตุผลที่กล่าวมา สรุปได้ว่า “การได้ตัวอ่อนระยะบลาสโตซิสต์มีโอกาสในการตั้งครรภ์สูงกว่า”